Modern Challenges and Innovative Tools for Sanctions Compliance



 16.06.2025
16.06.2025
 10 min read
10 min read
Challenges of Sanctions Compliance
Financial institutions need to meet growing sanctions compliance demands without disrupting customer services, incurring an exorbitant overhead, and being exposed to regulatory fines.

Regulators strongly encourage financial institutions to employ a risk-based approach to sanctions compliance by developing, implementing, and routinely updating a sanctions compliance program (“SCP”). While each risk-based SCP will vary depending on a variety of factors—size and sophistication, products and services, customers and counterparties, and/or geographic locations—each program should be predicated on and incorporate five essential components of compliance:
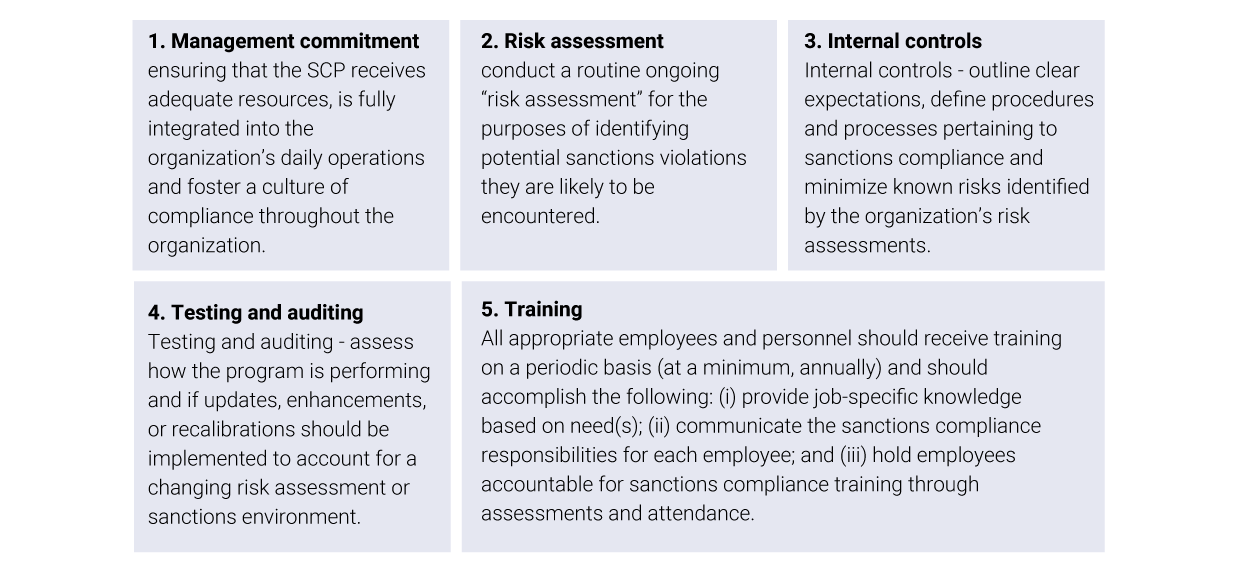
Sanctions screening involves reviewing individuals, organizations, vessels, aircraft, and geographical jurisdictions listed in transactional data, employees and contractors, and customer KYC information, followed by vetting them against country-based and list-based sanctions. Country-based sanctions reflect embargoes, such as the embargo on Cuba, while list-based sanctions focus on individuals and entities, such as terrorists. Sophisticated name checks and list screening tools are instrumental in determining if there is a connection with a sanctioned individual or entity. Hefty fines against financial institutions for failing to comply with AML laws and regulations have increased in recent years and is testament to the growing difficulty of adhering to sanctions compliance. Penalties and fines not only affect financial institutions’ net value, but also their reputation.
While robust filtering technology is essential to staying compliant, the most cost-effective approach combines intelligent technology, people, and processes with self-learning. Effective technology must have the capability to self-learn, which will systematically decrease the number of “False Positives.” Precise and cost-effective controls meeting the demands of regulators and customers will form an integrated sanctions compliance program. The onus is on financial institutions to detect, measure, and accept risk(s), and it is a fine balance to find solutions that are effective and efficient in monitoring and screening transactions. Areas of Sanctions Technology:
• Lists: criteria and technology processes to ensure that lists are only screened against a subset of data relevant to a specific jurisdiction• Exclusions: exclusion of a party from screening that poses low sanctions risk or the use of conditional screening rules using list data or source data attributes
• Suppression: use of suppression rules or “Good Guys” lists to manage common false positive alerts requiring unnecessary manual review. Suppression rules help reduce false positives by
applying very specific logical conditions before generating an alert. On the other hand, “Good Guys” lists work by suppressing unnecessary alerts on previously known false positives.
• Data: Data Attributes are specific pieces of identification information included in the Firm’s Reference and Transaction Data. The screening requirements for Data Attributes are categorized in three ways:
Strong data governance/management processes are imperative to reducing the noise. If the data is frequently incorrect or not available, financial institutions should consider improving data quality. Poorly configured screening software is often a contributing factor for regulatory fines. This is leading many financial institutions to abandon manual reviews and outdated sanctions screening systems in favor of more customizable and sophisticated technologies. This framework is also helpful during the vendor selection process for the financial institution’s Sanctions screening program.
Other factors to consider when selecting a vendor for screening software are:
• Transactional Volume
• Technology Synergy
• Repository of Matching algorithms
For larger or more complex financial institutions, there is an expectation that the screening program will require the use of a technology application that includes certain core functionalities to ensure appropriate alert creation by, and governance over, the screening process. Such functionalities include the capability to implement risk-based screening rules, generate high quality alerts for review, provide applicable metrics and reporting, ensure data integrity, and facilitate independent testing and validation. A robust operating model employs expertise from IT, Operations, and Financial Intelligence Unit (“FIU”) working together to ensure appropriate alert generation and disposition.
The figure below details the key components of a technology framework that are critical in the success of a robust SCP:
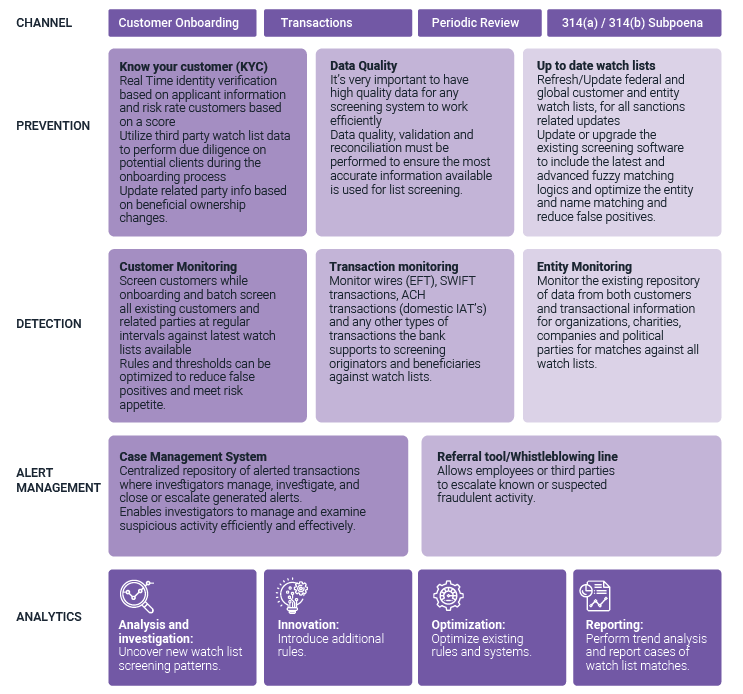
In 2014, OFAC’s amended its “50 Percent Rule” to state that the property and interests in property of entities directly or indirectly owned 50 percent or more in the aggregate by one or more blocked persons are considered blocked. OFAC “urges caution” even when an SDN has significant ownership under 50 percent, or an entity is controlled (but not owned 50 percent or more) by one or more blocked persons. This presents its own challenges as financial institutions need to ensure that they have a proper KYC process in place to identify related parties of the entities, and ensure that they are screened as part of the screening program.
The burden of finding these bad actors, equates to a range of tools and budgets for a comprehensive and robust Sanctions Compliance program at financial institutions. Institutions must invest in new and sophisticated technologies capable of automatically screening huge volumes of transactions and precisely identifying suspected violators. This adds a layer of complexity as financial institutions need a watchlist management system to review, update, and monitor any changes in the various watchlists.
Sanctions screening involves reviewing individuals, organizations, vessels, aircraft, and geographical jurisdictions listed in transactional data, employees and contractors, and customer KYC information, followed by vetting them against country-based and list-based sanctions. Country-based sanctions reflect embargoes, such as the embargo on Cuba, while list-based sanctions focus on individuals and entities, such as terrorists. Sophisticated name checks and list screening tools are instrumental in determining if there is a connection with a sanctioned individual or entity.
While no sanctions screening tool is perfect, it is important to understand the limitations of its technology. Risks and their risk mitigation controls should be appropriately assessed and documented by performing an impact assessment.
To validate the effectiveness of their compliance program, financial institutions should perform independent testing of their Sanctions screening technology. This usually involves passing a test dataset through the Sanctions screening tool in order to assess its effectiveness and the output data’s quality of “matches”. Additionally, the output should be evaluated to make sure that all the relevant critical fields (such as all available party name fields and country related fields within the transactions) are properly mapped and monitored by the Sanctions screening tool. The real-time dataset should be a sample of transactional data that will be tested in an environment similar to real-time screening in production at the institution; this sample should contain a homogenized mix of various transaction types and message types that are offered by the institution. Whereas the batch screening dataset should be a reasonable representation or synthetic data of the institution’s customer base, customer types, and geographies.
While testing the different screening capabilities (batch and real-time) provides the institution a level of confidence that all relevant data is processed by the screening solution, synthetic test data containing known name variations and typologies of sanctioned individuals/entities should be used to establish a benchmark for the screening solution. The results from the synthetic test data will provide the institution with an indication of the controls provided by the screening solution and assess if any additional mitigating controls or processes are needed based on the performance of the solution and the actual customer/transactional data. Not every screening solution is created alike, and the functionalities and algorithms are often black boxes that do not yield the same results when compared side-by-side. The financial institution must ensure that they have the methodology, testing artifacts, and other documentation available to demonstrate the “how” and “why” of the screening solution settings.
Due to the severity of fines associated with missed OFAC SDN matches by financial institutions, it is of great importance to ensure that there are no true positive hits that fall through the cracks. As such, modern sanctions solutions offers additional capabilities using more advanced algorithms and techniques to capture potential matches in addition to the traditional exact name matches.
The robustness of these new techniques however typically leads to higher numbers of false positives and requires a balance of risk tolerance in order to not overwhelm the capacity of investigations resources.
Regulators are looking for financial institutions to implement sufficient controls within their Sanctions Screening program, and it is the responsibility of the financial institution to have thorough knowledge of the risks associated with their products, geographies, and customers from both a qualitative and quantitative perspective – which is especially important now, given the dynamic and fast changing regulatory environment. An effective Sanctions Screening Program is a combination of policies, procedures, and technologies that enable a financial institution to ensure that it does not provide direct or indirect services to sanctioned parties, without a license and the approval of OFAC.
Matrix has helped global top-tier financial institutions implement, upgrade, and tune their sanctions and list screening solutions, with leading vendor solutions from Actimize, FircoSoft, Accuity, LexisNexis, and RDC. Our team consists of regulatory and technology subject matter experts, including former compliance executives and product development experts, with a strong foundation and deep understanding of compliance regulations, policies and procedures, and risk drivers to ensure these Sanctions compliance programs meet industry standards and regulatory expectations. The Sanctions framework developed by Matrix is solution agnostic and allows for easy identification of key Sanctions related risks at a financial institution based on their products and services, customer types, and geographies. Matrix developers have hands-on experience implementing out-of-the-box and custom tool features that fit the customer type and risk profile for these organizations. The expertise of both advisory and implementation experience across vendors ensures that the solution-specific functionalities are considered.






Extending AML Regulations to Investment Advisors
On August 28, 2024, the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) issued a final rule that extends Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) requirements to Registered Investment Advisers (RIAs) and Exempt Reporting Advisers (ERAs). This rule, effective January 1, 2026, mandates that RIAs and ERAs develop and implement comprehensive AML/CFT programs, aligning them with other financial institutions under the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA).

2024 Year in Review: Financial Crime Compliance, and Regulatory Trends
In 2024, regulatory enforcement increased, financial crime risks evolved, and scrutiny of both traditional and emerging financial institutions heightened. As regulatory bodies worldwide intensify their focus, organizations must adapt to a rapidly changing compliance landscape.
Databricks 2024 Developments and Announcements
The global Databricks Data + AI conference held two weeks ago in San Francisco included a long list of innovations and announcements. Unlike last year, this year Snowflake and Databricks held their conferences in the same conference hall (Snowflake first and Databricks a week later), giving data professionals and enthusiasts the opportunity to catch up, learn and attend an action-packed couple of weeks of announcements, expert presentations and networking..

Cloud AI and RPA
The fight against financial crimes has been on for decades. Do you remember Michael Night? Those of us who grew up in the good old days of the 80s were probably huge fans of the American action crime drama TV series, Knight Rider.

FINTRAC’s requirements – Armored cars
The Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre of Canada (FINTRAC) is Canada’s financial intelligence unit and anti-money laundering and anti-terrorist financing supervisor. Its mandate is to facilitate the detection, prevention and deterrence of money laundering and the financing of terrorist activities, while ensuring the protection of personal information under its control.
Using Generative AI in Combating Financial Crimes
Amazon recently launched a feature where hundreds, and sometimes thousands, of reviews are summarized into a concise and simple paragraph. This auto-generated summary allows the customer to instantly get an overall review of a product’s capabilities as well as overall customer satisfaction. This is a great example of using Large Language Models (LLM) to process and produce text that resembles that of humans. These models can understand language structures, grammar, context, and semantic linkages since they have been trained on enormous amounts of text data.
Evolution of DeFi Amid Regulatory Uncertainty
Emerging technologies are reshaping the financial services industry. On one end of the spectrum, initiatives such as Real-Time Payments and ISO20022 are modernizing existing payment infrastructure, making it faster and more efficient. On the other end, blockchain and distributed ledger technologies (DLT) are laying the foundation for an alternative ecosystem involving digital assets and cryptocurrencies.

Balance Open Banking Enthusiasm with Caution
Digitalization and Open Banking are two most prominent trends in banking industry in recent time. While the former was initiated by changing customer behavior, the latter was driven by regulatory and market forces.
Open Banking is a new kid on the block with a lot of promise and fanfare, but it can present new challenges for financial services. Rather than being swayed by its exuberance, a cautious approach is required for its implementation.

Combating Fraud – A Journey From Good to Great
Financial Institutions are in a similar situation. A lot has changed in the last few years. Fraud activities and losses are on the rise. FIs need to act or face the consequences – higher fraud losses, loss of public trust and declining customer loyalty. Given the risk, it is imperative that risk leaders adjust their fraud strategies to adapt to the new reality.

Banking & Compliance Post Pandemic
Traditional banking and the wind of change are not inherently linked, but now more than ever, it seems that the change offered by modern technology is not only adopted, but due to the pandemic is happening at an accelerated pace. From the demand for more speedy processes, through the increased trend of closing branches, and all the way to new possibilities that the digital arena offers (including AI and Machine Learning). All this without even mentioning Crypto and the challenges it posts to traditional banks. Weather we like it or not, change is all around us. Here are some highlights from our recent webinar where we discussed banking and compliance post pandemic:

Understanding Economic Sanctions
Imposing economic sanctions is a powerful foreign policy tool used by countries and international organizations that can include travel bans, asset freezes, arms embargoes, and trade restrictions with countries, individuals, and entities. The US Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) “administers and enforces economic and trade sanctions based on US foreign policy and national security goals.” The names of individuals, entities, aircraft, vessels, and countries are incorporated into OFAC’s list of Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons (“SDN list”), which blocks U.S. persons from transacting with both them and their assets. The SDN list is updated ad-hoc, with new additions to and removals from the list.

Navigating Emerging Risks and Regulatory Changes with a Robust AML Compliance Program
Regulators have fined financial institutions close to 20 billion dollars for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) shortcomings and regulatory violations in the last 6 years.

Matrix-IFS and Quantifind Partner to Complement Financial Crimes Solutions and Services
Quantifind, a provider of a SaaS platform used by banks to help automate financial crimes risk screening and investigations, today announced its partnership with Matrix-IFS, the leading provider of financial crime advisory and implementation services. Quantifind’s Graphyte™ platform brings best-in-class risk assessment and entity resolution accuracy to Matrix-IFS’ comprehensive services for KYC/CDD/EDD, transaction monitoring, sanctions screening, and case management. Graphyte includes integrations with leading case management platforms that seamlessly incorporate advanced risk intelligence directly within analysts’ familiar tools and workflows.
The Benefits of AML Cloud Convergence – AML as a Service
Many Chief Compliance Officers at midsized financial institutions sense that streamlining their anti-money laundering systems will lead to increased efficiency and effectiveness across their AML programs, but they wonder where to start.

How Mid-sized FIs Can Turn 3 Industry Trends into AML Opportunities
Midsized financial institutions (with $1 billion – $10 billion in assets) play an important role in our financial system, especially in the U.S. where banks with less than $10 billion in assets represent 14% of the market and 97% of the total number of banks.

Step 3 – Entity Resolution (Account Matching & Linking)
Welcome back to Matrix AML Academy. In case you missed our previous post, this is the 3rd part of an 8-part educational program on how to improve tour AML program and systems

Step 2 – Proactive Data Quality Automation
Welcome back to Matrix AML Academy. In case you missed our previous post, this is the 2nd part of an 8-part educational program on how to improve tour AML program and systems

Step 1 – Transaction Monitoring Implementation Best Practices
Welcome to Matrix Academy! A place you can hone in on your AML skills, gain valuable knowledge, learn insider tips of the trade and keep up to date with current technologies and methods

COVID-19 Cyber Security Risks & Remedies
As COVID-19 continues to spread, phishing lures related to the CoronaVirus continue to appear. Some instances of “Casebaneiro Banking Trojan”, “HawkEye” and “WSH RAT” all using COVID-19 in phishing lures or executable names were spotted.

The NY DFS 500 Cyber Security Regulation Requirements Checklist
The New York State Department of Financial Services (“DFS”) has been closely monitoring the ever-growing threat posed to information and financial systems by nation-states, terrorist organizations and independent criminal actors.

Matrix-IFS Expands Its Financial Crime Advisory Practice
Matrix-IFS, a specialized financial crime and compliance solution provider, announces the expansion of its Advisory Services with the acquisition of a leading NYC-based Advisory consulting firm, Alius.

Matrix-IFS Named “10 Most Trusted Risk Management Solution Providers” in 2019
With millions of accounts containing people’s life savings, security has always been one of the largest concerns for financial institutions and their customers. As cybercriminals become more sophisticated in their hacking techniques, institutions should adopt more advanced cybersecurity and fraud prevention systems. Although new technologies provide more advanced security options, knowing which ones to use and how to implement them is a challenge many institutions face today.

Hunter – The Historical Transaction Lookup Digital Investigator (RPA BOT)
Looking up historical transaction data is a task every Investigator knows and dreads; constantly going to the upstream data systems, collecting historical data, merging it, only to try and make sense how the customer behavior looks like. Imagine a world where he wouldn’t have to do all that and simply focus on investigations. Sounds like a dream, right? Not anymore. With Robotics Process Automation it is now a reality, one that could easily and quickly be adapted.
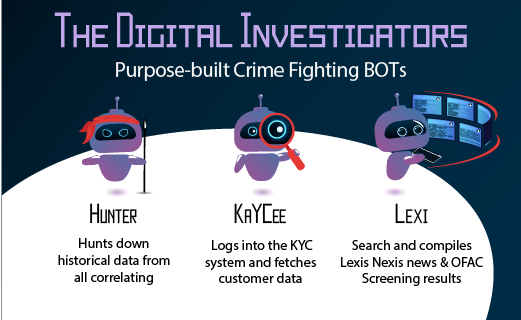
Unveiling Hunter, Kaycee & Lexi – AKA, the Digital Investigators
On October 10th, we had the honor of speaking at the European Banking Forum in London in front of 100 compliance & financial crime Senior Managers, where we announced our purpose-built Digital Investigators into the world.

A Word About Cost Conscious Compliance
Last week, we had the honour and pleasure to engage in a fruitful conversation with a roomful of Compliance leaders from the financial sector, to share ideas and findings as to practical approaches to reducing compliance overheads.

Crime Tourism – ATM Skimming Operations
We’ve all been there, choosing our next travel destination. What should be a fun and exciting experience, can sometimes be stressful and overwhelming as there are many factors that can impact on our choice of a travel destination, to name a few: budget, travel companions, timing, weather and popular attractions.

Matrix-IFS is Sponsoring ACAMS Europe in Berlin (June 12-13 )
On June 12th, Matrix-IFS will be taking part in one of the most prestigious Financial Crime Conferences in Europe – ACAMS Europe, which will take place at the Berlin Congress Center GmbH. This 2-day conference brings together vendors, industry thought leaders and various financial institutions from across Europe.

The 5th AML Directive Readiness Checklist
During 2019-2020, EU countries will pass laws that introduce the 5th AML Directive (5MLD) into their respective national laws. Now is the time for your organization to invest in improving and optimizing your existing AML solutions to meet the increased challenges and regulator demands before it’s too late.

Best Practices to Transaction Monitoring Implementation
There are four key phases in transaction monitoring (TM) implementations and how a bank should design and execute these phases. Successful implementation of rule selection, data prep, segmentation, tuning and operational optimization will determine the success of the overall TM implementation in your organization.

Matrix-IFS is Attending ACAMS Florida (April 15-17)
On April 15–17 Matrix-IFS will be taking part in one of the largest Financial Crime Conferences in the US – ACAMS Florida, which will take place at the Diplomat Resort & Spa in Hollywood, Florida. This 3-day conference brings together vendors, industry thought leaders and various financial institutions from across the world.

The Problem with AML Today & How to Fix It: Part I – The AML Problem
The latest discoveries around the massive scale of money laundering at Danske Bank and ING are just two of the most recent examples of an underlying problem with the Anti-Money Laundering (AML) discipline. Despite increasing efforts and investments focusing on the AML problem, money laundering techniques continue to evolve and evade the controls implemented by Financial Institutions (FIs). More and more industry voices decry the efficiency and effectiveness of the current AML approach – which entails running all transactions through a series of automated checks to spot anomalies based on a large set of pre-defined typologies provided by experts.
Applying Robotic Process Automation in AML & FIU Operations
Learn how RPA can increase efficiency, lower risk, and trim your overhead

Matrix-IFS Hosts 4 Anti-Financial Crime Webinars
Matrix-IFS introduces a series of timely and informative webinars on new issues, trends and solutions in Anti-Financial Crime. Webinars are designed to update and inform risk, compliance, control room and fraud professionals working in financial institutions and capital markets.

Supercharge your FIU’s Operations with RPA at ACFE Las Vegas
During The 29th Annual ACFE Global Fraud Conference Anshul Arora , Head of FL Delivery Center will present Matrix-IFS’s RPA solution for improved operations and increased efficiency. During his session, Anshul will explore a new vision of a modern FIU department, which incorporates Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and advanced analytics to address and reduce alerts as well as how robotics and automation can play part in reducing risk and simplifying the work of the Investigators.

Top 6 Deal / List Systems Challenges and How to Solve Them
You know the challenges associated with your Deal Management (DMS) and List Management (LMS) systems & processes. You may even be aware of the full burden and cost they pose to your department and your organization. Now benefit from the fresh approach firms are taking with their Deal and List Management systems to gain efficiency and save time and resources.

How to Overcome AML Operations Growing Pains Using Cutting-edge Technology? | Find Out at ACAMS Europe
During ACAMS Annual Europe Conference taking place 30 May – 1 June in Amsterdam, Matrix-IFS will participate in a panel session on the subject of AML Operations and how to fight growing pains using cutting-edge technology where we will share options to enhance performance by replacing limiting rule-based solutions with far more efficient intelligent solutions that operate within existing infrastructure.The panel will discuss combining Graph Analytics, AI/Machine Learning, and Scenario Authoring on big data to improve the quality of detection, prevention and reporting of financial crimes.

Future-Proofing Financial Crime Compliance: A Technology Blueprint for Smarter Risk Management
The evolution of threats to the financial system is outpacing advancements in Financial Crime Compliance (FCC) regulations and technology used by financial institutions (FI). In this situation, FI can save considerable funds, by creating or evolving their business architecture with a view of adapting to emerging threats and the advanced tech that will be required to tackle them.

Matrix-IFS Named “Top 10 Risk & Compliance Solution Providers 2018”
Since 2006, Matrix International Financial Services (Matrix-IFS) has been helping financial institutions strengthen business compliance and address financial crimes and fraud issues, with a goal to satisfy both regulators and clients with effective, efficient and cost-effective solutions.

Deciphering Multi-Faceted Venezuelan Sanctions – Top Ten Practical Tips to Stay Compliant
The recently imposed Venezuelan sanctions issued by the U.S., the E.U., and Canada have placed heavy burdens on sanctions compliance programs. This has made it…
Quick answers. Real solutions.
Let’s Connect and Explore How We Can Help
Fill out the form and our team will get back to you shortly.

Quick answers. Real solutions.
Let’s Connect and Explore How We Can Help
Fill out the form and our team will get back to you shortly.
 Thank you!
Thank you!
Please submit your details
